How private 5G helps industries tackle critical challenges
Why industries are embracing private 5G
The fourth industrial revolution (4IR or Industry 4.0) is transforming the way businesses operate, unleashing digital innovation across sectors. Many industries already use private WiFi or LTE networks. The next step for enterprises to unlock the potential of 4IR is implementing private 5G networks.
Private 5G, or non-public network (NPN) as it is called according to 3GPP, equips enterprises with next-gen connectivity over a secure and dedicated network, enabling the smart features of 4IR. It lets businesses gain the most benefits from implementing breakthrough Industry 4.0 technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, robotics, AR/VR, and more. In addition to fully automating processes, private 5G provides high capacity, near-real-time high-speed connectivity, ultra-reliable infrastructure, and high-end computerization. In effect, enterprises of any size and operational capability can drastically improve their efficiency and lower OPEX.
Today, deploying a secure private 5G network is significantly easier owing to several factors. For one, Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) enables shared wireless spectrum in the United States, a model that’s being replicated by many other countries. New 5G standards define how these networks can be implemented. And there’s mature software as well as hardware, including an open ecosystem for RAN and core network components. Plus, with the growing number of connected devices on enterprise networks, private 5G assumes even greater relevance. It enables businesses to securely gather, analyze, and act upon data, leveraging AI, ML, and robotics.
Benefits of private 5G for enterprises
Businesses across sectors gain several unique benefits from deploying 4IR technologies over a private 5G network:
Enabling smart factories
Private 5G lets enterprises implement cutting-edge technologies such as AI, augmented reality, predictive analytics, robotics, autonomous vehicles, and a connected Industrial IoT (I-IoT) device ecosystem. Together, these technologies enable them to gather and analyze data in real time, streamline production and business processes, predict outcomes to refine and fine-tune activities, and ultimately boost productivity.
Deploying wireless infrastructure
A key benefit of private 5G is that it eliminates bulky cables and wires, delivering next-gen capabilities over an entirely wireless network. This is a game-changer for capital-intensive enterprises that can implement capabilities like low latency, high reliability, and consistent connectivity
while keeping operational costs low. Private 5G is also much more secure and reliable than WiFi or LTE. It enables enterprises to maintain an agile and flexible environment for their business-critical activities, with infrastructure that’s easy to develop, configure, and maintain.
Improving operational efficiency
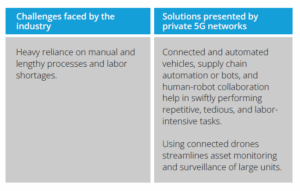
Private 5G helps minimize and eliminate delays or errors due to human intervention. It enables businesses to efficiently manage supply chains, improve quality checks, ensure worker safety, and more. For example, a smart factory with a private 5G setup can work faster with the help of robots and other connected devices than traditional factories that follow labor-intensive manual processes.
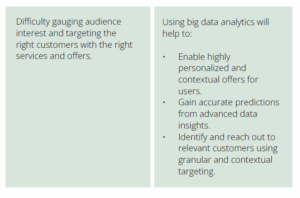
Gaining advanced data insights
Private 5G helps drive sound business decisions in real-time by leveraging data and advanced analytics to gain intelligent BI insights. For instance, 5G features such as high throughput, lower latency, and ultra-reliable communication, along with proven AI capabilities, help in building an intelligent transportation system that facilitates seamless planning, real-time alerts and notifications, coordinated driving, and flawless C-V2X communication.
Increasing security
Industrial IoT has massive volumes of connected devices, all of which are susceptible to new kinds of security threats. To keep them safe from cyberattacks, vulnerabilities, and other breaches, private 5G provides added layers of security and enhanced privacy protection. 5G also employs robust security algorithms, traffic encryption, and signaling and interface protection, making it safer and more secure than LTE and WiFi.
Optimizing network resources
Unlike other legacy networks (3G, LTE, or WiFi), 5G enables network slicing and optimization, which helps support mission-critical use cases such as drones, digitally connected device management, human-robot collaboration, digital twins, and much more. Each of these use cases has specific requirements, and slicing lets operators divide the network into multiple smaller fragments or slices, each of which caters to the demands of different use cases. To optimize resources, different slices can be allotted to separate enterprises.
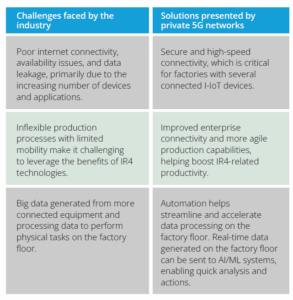
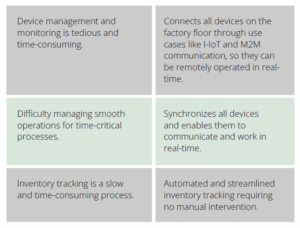
Industry pain points and how private 5G will tackle them
Private 5G helps cater to data-heavy applications like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to remotely monitor systems, improves data security, and provides secure 3GPP-defined infrastructure for mission-critical services and government applications. It has the potential to provide reliable wireless connectivity to modern factories, ports,
warehouses, oil rigs, mines, sports stadiums, classrooms, hospitals, and broad-spectrum applications such as public utilities – the list is endless.
Here are some of the key industries expected to embrace the next-gen technology and the challenges it will help them overcome.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing units can benefit significantly from infrastructure and applications that provide high levels of reliability, ultralow latency, consistent and secure connectivity, and a low physical resource footprint. These capabilities help ensure they can smoothly run their business-critical activities. Private 5G delivers on all fronts.
Manufacturing units can leverage private 5G to implement innovative use cases like robotics, AI, I-IoT, AR, and more. These technologies transform production processes so manufacturers can improve operational efficiency, minimize production downtime and delays, streamline supply chain management, ensure more efficient quality checks, and improve the safety of factory staff.
Transportation
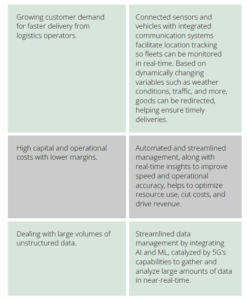
Cities with 5G access will be able to transform their transport systems, reducing traffic congestion and improving vehicular as well as pedestrian safety. Private 5G will improve the overall efficiency of public transport, enabling real-time fleet monitoring and analyzing user demand to optimize management. In fact, public mobility-driven demand for advanced business models such as mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) will likely be an important 5G revenue stream for operators. At the same time, public transport commuters will have more control over their trips online, as well as access to contextual offerings.
Commuters will also be able to access safe and reliable public transport services, choosing the optimal option based on real-time traffic changes. While onboard, they will have access to information, infotainment, and entertainment, as well as improved connectivity to first-responder services in case of emergencies.
In addition, smart cities will be able to connect road infrastructure such as traffic lights to enable more streamlined traffic management.

Use cases:

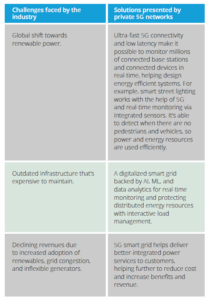
Energy and utilities
Private 5G-IR4 deployments will be transformative for the public utilities and energy sector, which have long been struggling to overcome infrastructural issues. These next-gen deployments will combine ML, AI, and advanced analytics to enable more control over the way energy is stored and distributed. Implementing modern use cases such as smart metering, smart grid, smart energy management, and predictive maintenance will help reduce operational and maintenance costs, securing revenue. They will also enhance the customer experience to meet and exceed expectations from an ever-evolving market.
Use cases:

Healthcare
By leveraging private 5G, healthcare providers can give patients access to more efficient and personalized treatment. Teleconsultations and remote surgeries broaden the horizon of care options open to patients even in distant and underserved areas as they remove geographical barriers. Private 5G networks enable ultrafast speeds, uninterrupted connectivity, ultralow latency, and real-time streaming to enable these applications, broadly classified as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). These technologies will become more broadly available once IoT-enabled automation and private 5G become permeate.
Use cases:
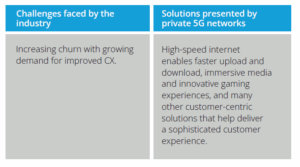
Banking and financial services
Today, the success of financial services such as banks, finance, and insurance (BFSI) companies is hinged, among others, on two important factors: security and customer experience. Private 5G helps fulfill these two requirements by providing ultra-high reliability, higher data capacity, and low latency. The adoption of private 5G and more widespread use of IoT systems and devices will help boost security and CX while driving ROI.
Entertainment and media
5G technology will change the face of entertainment and media, with multiple applications across broadcasting and media production. As more smartphones and consumer devices support rich media and advanced audio, video, and multimedia experiences, entertainment providers will be able to use the low latency and high bandwidth abilities of private 5G networks to enable more enriching experiences. These new media experiences can be exclusively developed to cater to different residential and enterprise clients through collaborations for shared live entertainment, interactive gaming, enhanced mobile advertising using videos and banners, and much more. Private 5G can also be deployed as a temporary network for live events such as sports and music festivals.
Use cases:
Education
The pandemic accelerated a massive digital revolution in education, with more students and educators adapting to the use of virtual classrooms and e-learning platforms. 5G will further bridge the education divide by overcoming the limitations inherent to legacy networks with ultrafast speeds, immersive experiences, seamless connectivity, and more. It will integrate IoT and robotics to empower educators to create unique experiences that are as good as or even better than the physical classroom.
Use cases:
Agriculture
Private 5G will be revolutionary for agricultural communities, and streamlining agricultural practices will eventually benefit the end consumer with higher quality products at lower costs. Many agricultural experts are already monitoring and improving farming practices by implementing newer technologies along with devices like drones, sensors, and cameras. By introducing a private 5G network into the equation, they will be able to ensure more precise and efficient processes.
Use cases:
Logistics
The applications of private 5G in the logistics sector are multifold. Logistics operators will be able to introduce autonomous vehicle fleets and streamline planning and processes by enabling more connected devices. They will be able to drastically reduce costs and increase operational efficiency. They will also be able to track goods in real time across the logistics chain. Further, they can streamline operations and improve monitoring across ports, logistics centers, and more.
Use cases:
Moving forward: how to monetize private 5G networks
Private networks deployed on licensed spectrum help ensure QoS over the wireless medium, and licensed spectrum can essentially be acquired through mobile operators. While larger enterprises are choosing to set up their own local 5G networks, many others, especially small and medium ones, will partner with operators. To attract more partners, 5G service providers will need to enable innovative next-gen use cases across sectors.
Over time, we can expect more standardization of NPNs, and while this will make deployments somewhat easier, what will be a differentiator for enterprises will be the operator’s network design expertise in the sector. Zeroing in on a few specific verticals and specializations will likely be a profitable business approach.
Another monetization opportunity MNOs can consider is moving away from end-to-end network deployment and instead focusing on singular models such as leasing spectrum, providing multi-site network connectivity for government bodies or larger enterprises, offering guest 5G plans for hotels and cafes, and more.
Alepo has been an early mover in implementing 5G and private 5G networks. It provides key components of the 5G core and has partnered with global technology leaders to provide an end-to-end solution to fulfil diverse business requirements. It enables operators to deploy their NPN over the licensed spectrum and slice the network to support diverse industry applications.
Begin your 5G journey today: market.development@alepo.com